How to Plan the Harvest Throughout the Seasons for Sustainable Harvesting

Understanding Seasonal Harvesting
The art of harvesting stretches beyond simple collection; it plays a pivotal role in sustainable agriculture. Adapting harvest schedules to align with the changing seasons not only enhances crop productivity but also contributes to environmental stewardship. This intricate dance between agriculture and nature acknowledges that timing is crucial, not just for the farmer’s profitability but for the health of ecosystems as a whole.
Key Benefits of Seasonal Planning
When farmers effectively plan their harvests throughout the seasons, they position themselves to reap numerous advantages. These benefits include:
- Maximized crop yield: Crops harvested at their ideal moments result in better taste, nutrition, and quantity. For instance, tomatoes picked just as they reach peak ripeness tend to have higher sugar content and flavor, making them more desirable in the market.
- Reduced waste: Timing plays a critical role in minimizing overripening and loss. For example, if a farmer delays the harvest of pumpkins until they have begun to rot, the entire crop can be compromised, leading to significant financial losses. Proper scheduling can ensure that produce reaches consumers while still fresh.
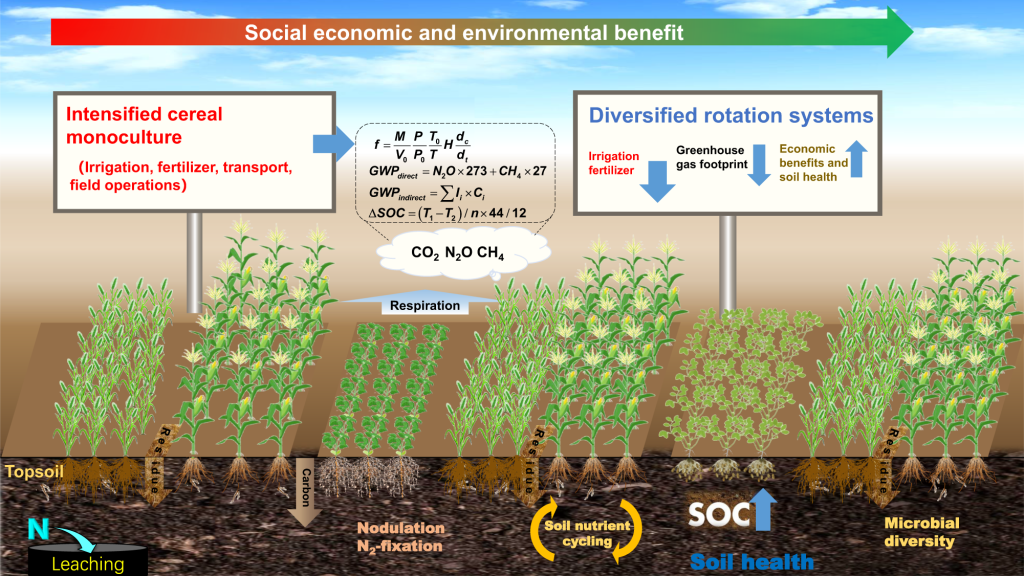
- Soil health: Crop rotation is not only a traditional practice; it also supports soil health. Alternating between crops, such as utilizing legumes one season and corn the next, can replenish nutrients and prevent soil depletion, ultimately leading to healthier yields over time.
Strategies for Sustainable Harvesting
To enact a sustainable harvest, farmers must develop clear strategies that can adapt to varying climatic conditions and crop types. Key elements include:
- Monitoring local climate: Keeping abreast of short and long-term weather patterns is essential. For example, an unforeseen frost in early spring can impact the growth cycle of fruits like strawberries. By utilizing weather apps, farmers can predict seasonal changes more accurately.
- Crop rotation practices: Incorporating diversity in planting not only helps maintain ecological balance but also combats pest issues and diseases. For instance, rotating cotton with peanuts can break the life cycle of pests that favor one or the other.
- Utilizing technology: Today’s farmers have access to advanced agricultural technology. Applications that track plant growth or drones that provide aerial insights can significantly enhance operational efficiency, allowing farmers to make informed decisions about their harvest.
Embracing these sustainable practices not only ensures successful harvests but also nurtures the land for future generations. The importance of understanding seasonal harvesting reaches far beyond immediate results, resonating deeply with the growing consumer demand for locally sourced and sustainably produced food. In a world where climate change poses increasing challenges, gaining insights into seasonal planning can empower farmers and enthusiasts alike to support both agricultural viability and ecological integrity.
Dive deeper into the nuances of seasonal planning to discover how to balance productivity with sustainability. By aligning agricultural practices with nature’s rhythms, we can cultivate resilience not only in our crops but also in our communities and environments.
DIVE DEEPER: Click here to learn about drip irrigation techniques
Establishing a Seasonal Harvest Calendar
To successfully plan for sustainable harvesting, farmers must first create a detailed seasonal harvest calendar. This essential tool serves as a roadmap, guiding the timing of planting, nurturing, and ultimately, harvesting crops. It should account for local climatic conditions, crop life cycles, and market demand, ensuring that each crop reaches its prime quality before being harvested. A well-structured calendar not only enhances the efficiency of farm operations but also maximizes the potential for revenue generation and environmental sustainability.
Key Components of a Harvest Calendar
A comprehensive harvest calendar should include various elements critical to ensuring a successful yield. Some of these components are:
- Planting schedules: Detail the optimal planting times for each crop based on historical weather data and soil temperature recommendations. For example, understanding that carrots thrive when planted in early spring can make a significant difference in lead time before harvest.
- Growth milestones: Tracking the growth stages of crops is vital. Farmers should note when plants reach key milestones, such as flowering or fruiting, as these will indicate when to begin monitoring for ripeness. Implementing a weekly observation routine can assist in this process.
- Harvest dates: Predetermined harvest dates should be adjusted as needed based on real-time observations and weather conditions. It is important to consider the unique characteristics of each crop; for instance, leafy greens like spinach can wilt quickly once they reach full maturity, so timing their harvest accurately is crucial.
- Market considerations: Stay informed about market trends and consumer preferences. For instance, early-season strawberries often command higher prices, incentivizing farmers to plan their harvest accordingly. Access to local buyer networks and farmer’s markets can aid in understanding demand fluctuations.
Assembling this information requires a keen eye for detail, as well as assistance from reliable agricultural tools and resources. Utilizing local cooperative extensions or agricultural universities can provide invaluable insights tailored to specific regions within the United States, enhancing a farmer’s ability to adapt their practices accordingly.
Integrating Crop Variety for Resilience
Diversifying crops is a cornerstone of sustainable harvesting, contributing to both ecosystem stability and economic viability. A varied crop selection improves the resilience of farmland against pests, diseases, and climate variability. For example, the incorporation of cover crops like clover or rye can provide multiple benefits: they enrich the soil, manage erosion, and suppress weed growth during off seasons. Furthermore, farmers who choose to plant a mix of fruits, vegetables, and grains can stagger harvest times, spreading labor demands and reducing peak harvest pressure.
The synergy between knowing the ideal time to plant, nurturing the crops, and anticipating harvesting windows allows for a more streamlined approach to sustainable harvesting. As farmers embrace these strategies, they not only fortify their own operations but also contribute to a more sustainable food system that can adapt to the numerous challenges presented by changing climatic conditions and fluctuating market dynamics.
Understanding Seasonal Harvesting Techniques
Harvesting sustainably throughout the seasons is not just about timing; it’s about understanding your crops, local climate, and employing smart techniques. Seasonal analysis is vital to optimize yields and reduce waste. Throughout the year, conditions change significantly, affecting both the quality and quantity of harvests. By analyzing these seasonal shifts, farmers can implement methods that align with their specific growing conditions.
One effective technique is crop rotation, which helps to replenish soil nutrients and reduce pest problems. During winter, cover crops such as clover and vetch can be planted to enrich the soil and prevent erosion. In spring, focus on harvesting early crops like lettuce or peas, which thrive in cooler temperatures. The summer season then requires vigilance with crops that can quickly perish if not monitored closely, such as tomatoes and peppers.
Finally, as autumn approaches, implementing proper storage techniques becomes crucial. Post-harvest handling, which includes cleaning, drying, and storing produce, can significantly extend the shelf life of your harvest. Techniques such as these not only support sustainability by minimizing waste but also help ensure that crops provide nourishment well beyond their harvest period.
| Category | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Crop Rotation | Improves soil health by alternating crops. |
| Cover Cropping | Protects soil and enhances fertility during off-seasons. |
| Post-Harvest Handling | Ensures quality and longevity of harvested products. |
Adopting these practices not only fosters sustainable agriculture but also helps farmers adapt to changing environmental conditions. Ensure that you stay informed on best practices and continually adjust as needed to secure the bounty of each season.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here for essential soil tips
Implementing Sustainable Practices for Continuous Harvesting
A pivotal aspect of planning for sustainable harvesting lies in the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices. These practices not only contribute to the long-term health of the land but also ensure that crops can be harvested continuously throughout the seasons. By focusing on methods that respect and enhance the natural ecosystem, farmers can improve their resilience and adaptability in the face of environmental challenges.
Crop Rotation and Companion Planting
Crop rotation is a strategy that involves alternating the types of crops grown in a specific area over various seasons. This method can help to preserve soil fertility, reduce pest cycles, and minimize the incidence of diseases. For instance, following a nitrogen-fixing crop like legumes with nutrient-demanding crops such as corn ensures the soil remains nutrient-rich. Additionally, integrating companion planting, where specific crops are planted together to promote growth or protect against pests, can optimize yields. Planting basil alongside tomatoes, for example, can enhance flavor and deter pests naturally.
Soil Health Management
The foundation of sustainable harvesting starts with soil health. Farmers should regularly conduct soil tests to assess nutrient levels, pH balance, and microbial activity. Implementing practices such as organic composting, minimal tillage, and the use of cover crops can significantly improve soil structure and fertility. Incorporating organic matter into the soil enhances water retention and provides a diverse habitat for beneficial microorganisms, which play a crucial role in nutrient cycling. A well-balanced and healthy soil system results in healthier plants, leading to improved yields and more consistent harvesting opportunities.
Utilizing Technology for Precision Agriculture
In today’s technologically advanced world, precision agriculture offers innovative tools to enhance efficiency in farming operations. Utilizing GPS technology, drones, and soil moisture sensors enables farmers to monitor crop health and soil conditions more precisely. This data-driven approach allows farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest management, optimizing the harvest timeline. For instance, drones can assess plant health and pinpoint areas needing attention, allowing farmers to address issues before they escalate and impact yields.
Seasonal Adaptability Through Greenhouses and Polytunnels
Another effective option for extending the growing season and improving yield consistency is the use of greenhouses and polytunnels. These structures create controlled environments that allow for earlier planting and later harvesting, as they can shield crops from extreme weather conditions. Farmers can cultivate a greater variety of crops throughout the year—like tomatoes or cucumbers, which typically have shorter growing seasons—leading to a more consistent and varied harvest. This adaptability is essential in an era when climate patterns may become less predictable, allowing farmers to buffer against potential weather-related crop failures.
By combining these sustainable practices—crop rotation, soil management, technological advancements, and protective structures—farmers can significantly improve their operational efficiency. This holistic approach to planning harvests throughout the seasons ensures not only the sustainability of farming practices but also contributes to overall food security and a healthier ecosystem, making it a strategy worth exploring for farmers dedicated to responsible stewardship of the land.
DISCOVER MORE: Click here to learn about optimal watering frequencies
Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Harvesting for a Resilient Future
In conclusion, planning harvests throughout the seasons for sustainable harvesting requires a multifaceted approach that integrates best practices in agriculture, environmental stewardship, and technology. By emphasizing sustainable agricultural practices such as crop rotation, soil health management, and advancements in precision agriculture, farmers can create systems that are not only productive but also resilient to the challenges of climate change and soil degradation.
Moreover, adopting structures like greenhouses and polytunnels can extend growing seasons and enhance yield consistency, enabling farmers to diversify their crops and meet market demands year-round. This adaptability is vital in an unpredictable climate, providing farmers with a buffer against potential losses due to adverse weather.
Looking forward, it is essential for farmers, policymakers, and consumers alike to engage in continuous learning about sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts to promote education and research in sustainable agriculture will further empower farmers and communities to implement innovative strategies. By prioritizing sustainability in farming, we not only ensure the viability of agriculture for future generations but also contribute to the overall health of our ecosystems.
Ultimately, a commitment to sustainable harvesting can lead to greater food security, economic stability, and environmental integrity, making it a shared responsibility that calls for active participation from all corners of society. As we embrace these sustainable practices, we lay the groundwork for a resilient agricultural future that thrives in harmony with nature.
Related posts:
The Impact of Weather Conditions on Harvest: How to Adapt Your Garden to Climate Changes
Sustainable Harvest: Practices to Ensure an Efficient and Environmentally Correct Harvest Time
The Natural Signs That Indicate the Ideal Time to Harvest Herbs and Spices
The Synergy Among Plants: How Crop Rotation Influences Harvest Timing
How to Identify the Perfect Time to Harvest Fruits in Your Garden
How Climate Conditions Influence Harvest Timing in Home Gardens

Linda Carter is a gardening writer and home-growing specialist who helps beginners cultivate thriving home gardens. With extensive experience guiding new gardeners through plant selection and sustainable growing techniques, she shares practical gardening strategies on our platform. Her goal is to empower readers with actionable advice and step-by-step strategies to successfully grow their own food and create beautiful, productive gardens at home.